Expanded-scope CIPP liner tests
Expanded-scope CIPP liner tests
The minimum scope of testing for CIPP liners consists of the three-point bending test for determination of modulus of elasticity and bending stress, and the water tightness test.Further tests are available, as defined in the ZTV Materials Testing (CIPP liner test standards), which make it possible to determine the quality of CIPP liners even more precisely.
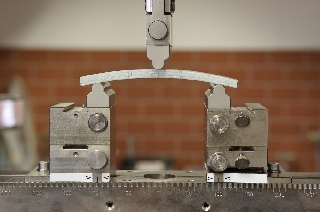
Three-point bending test
The three-point bending test (DIN EN ISO 178 and DIN EN ISO 11296, Part 4) is used to determine modulus of elasticity and bending stress at fracture (short-term modulus of elasticity and short-term bending stress).The thickness of the load-bearing wall of the CIPP liner, for which design criteria are available from the structural-analysis calculation and the contract documentation, is also determined.
Target values for the mechanical characteristics of “modulus of elasticity” and “bending stress” can be found in the national technical approvals for the CIPP liner method used.
An overview of the technically approved CIPP liner methods, including details of materials characteristics, can be found in the Annex to the ZTV Materials Testing (CIPP liner test standards).
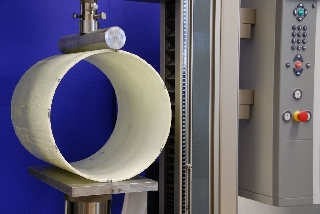
Vertical compression test
Initial ring stiffness and modulus of elasticity are tested in the vertical compression test (DIN EN 1228).The vertical compression test is nowadays usually performed for sewer-lateral liners and small diameter CIPP liners (DN 150 and less), since the taking of a complete pipe section, rather than a sub section is usually possible in such cases.
Alternatively, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis can be performed on small samples, in order to verify at least the curing of the resin, instead of the mechanical characteristics (see below).
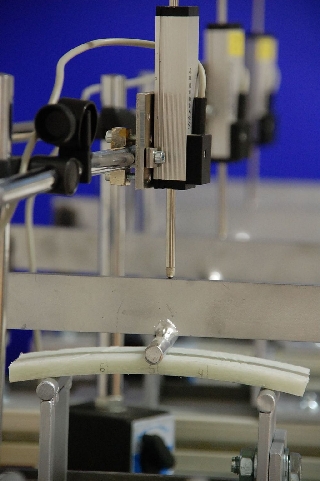
24-hour creep
This test can be performed as part of the three-point bending test or of the vertical compression test (DIN EN ISO 899, Part 2). The deformation of the sample across time under constant load is measured.The deformation of a CIPP liner under constant load becomes increases with time. This phenomenon is referred to as creep behaviour.
This is taken into account in the structural design of a CIPP liner by assuming the long-term characteristics data for modulus of elasticity and bending stress at fracture. These can be determined from the short-term values for the three-point bending test by means of the so-called reduction factor, which is stated in the DIBt approvals
Testing of 24-hour creep is performed to check, by exposing a sample of CIPP liner to load for 24 hours, whether the CIPP liner possesses the expected long-term behaviour.
In addition, this indirectly checks the curing of the CIPP liner as an incompletely cured liner sample will not meet the limits for 24-hour creep.
The target values for this can be found in the respective DIBt approvals.
Determination of residual styrene content
Polyester resin contains styrene, which is fixed after curing. The free (non-fixed) styrene content (residual styrene content) therefore provides information on the through-curing of a CIPP liner sample.Free styrene content is determined using a gas chromatograph after extraction using dichloromethane (DIN 53394, Part 2).
DSC analysis
Differential scanning calorimetry is a thermal analysis procedure, through which curing of epoxy resins can be verified (DIN 53765) using small samples (up to 20 mg).The glass transition temperatures TG1 and TG2 (° C) of a sample are determined in two heating operations. Enthalpy (J/g) is also stated. DSC analysis is used primarily in the case of sewer-lateral liners if site samples cannot be taken for performance of mechanical tests
Spectral analysis
Spectral analysis is used to determine whether the quality of resin installed conforms to the resin quality originally offered by a contractor.The infrared spectrum of the site sample is compared against a reference spectrum as specified in the DIBt approval (ASTM 5576, DIN 55673, with reference).
Every supplier of CIPP liners is required under DIBt approval to submit to the test laboratory a reference sample of his approved resin system.
Determination of filler and glass content
The textile glass and mineral filler content of a CIPP liner sample is determined by means of the calcining method (DIN EN ISO 1172).
Water-tightness test
The water tightness test is performed in the laboratory in order to determine whether the cured laminate of the CIPP liner is water tight (in accordance with APS Test and Inspection Code, ZTV Materials Testing, DWA-A 143-3).
Density
The density of a CIPP liner sample can be used to determine whether the liner has been adequately impregnated with resin. Any air inclusions present can cause leaks in the laminate (DIN EN ISO 1183, Part 1).The density of a CIPP liner sample is stated in the DIBt approval.
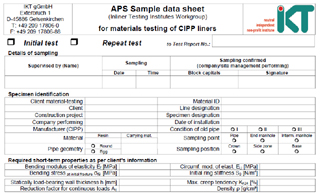
Sample data sheet
Materials testing of CIPP liners
Please enclose this form when you send us your samples. This ensures that your sample can be correctly identified.
Please complete a sample data sheet for each individual site sample you send us.
Sample data sheet for CIPP liners
Request for quotation
Materials testing of CIPP liners
Do you require standard or expanded-scope tests?
We will provide a quotation tailored to your needs, to ensure that your QA requirements are met.
Request for quotation CIPP liners
Contact
Dieter HomannDipl.-Ing.
T: 0209 17806-24
E: homann@ikt.de